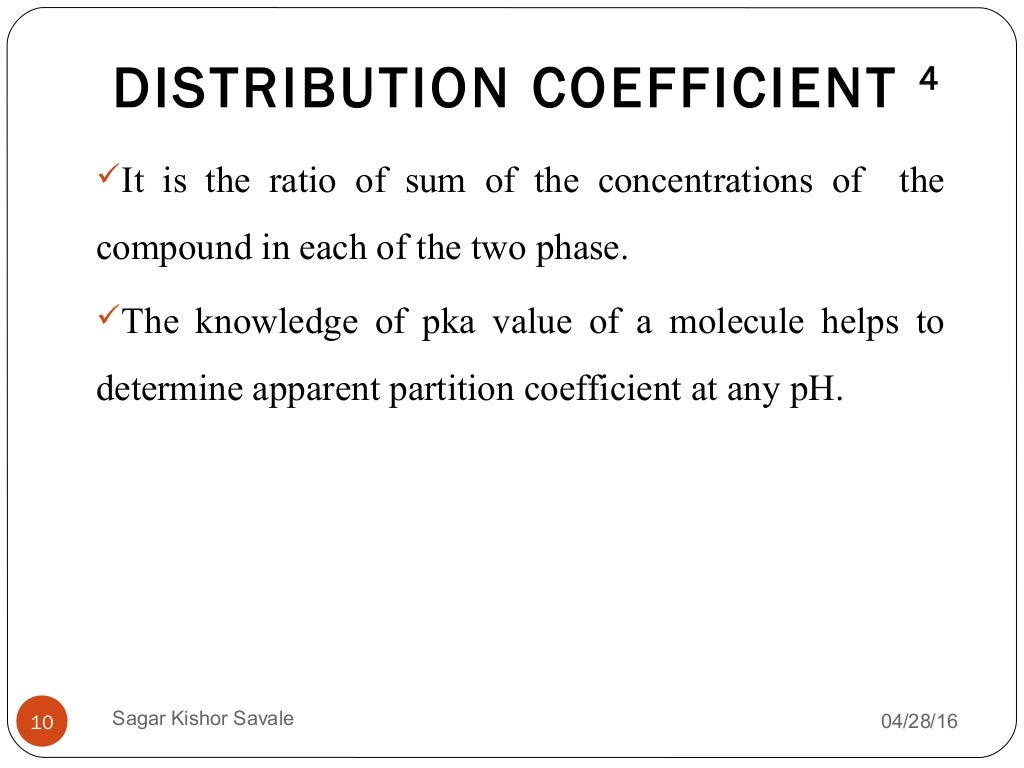
Partition Coefficient Explained . what is partition coefficient? the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to the aqueous layer. a partition coefficient is the ratio of a solute in two different solvents. in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a substance in one medium or phase (c 1) to the concentration in a second. Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two.
from www.slideshare.net
a partition coefficient is the ratio of a solute in two different solvents. a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a substance in one medium or phase (c 1) to the concentration in a second. the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to the aqueous layer. The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two. the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. what is partition coefficient?
Partition coefficient
Partition Coefficient Explained what is partition coefficient? the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. what is partition coefficient? Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to the aqueous layer. a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a substance in one medium or phase (c 1) to the concentration in a second. a partition coefficient is the ratio of a solute in two different solvents. The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two. in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/.
From www.slideshare.net
Partition coefficient Partition Coefficient Explained The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two. the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a substance in one medium or phase (c 1) to the concentration in a second. . Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lipinski’s rule of five PowerPoint Presentation, free download Partition Coefficient Explained the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. a partition coefficient is the ratio of a solute in two different solvents. a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a substance in one medium or phase (c 1) to the concentration in a second.. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Partition coefficients. Download Table Partition Coefficient Explained the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to the aqueous layer. a partition coefficient is the ratio of a solute in two different solvents. the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. a partition coefficient is. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Comparative analysis of Partition Coefficient (Vpc) and Partition Partition Coefficient Explained in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. what is partition coefficient? The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From studylib.net
Partition coefficient and partition calculations Partition Coefficient Explained what is partition coefficient? the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. the partition. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From thechemistrynotes.com
Partition coefficient (P)/ Distribution coefficient (D) Partition Coefficient Explained a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a substance in one medium or phase (c 1) to the concentration in a second. what is partition coefficient? the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to the aqueous layer. Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Partition Coefficients PowerPoint Presentation, free download Partition Coefficient Explained Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. what is partition coefficient? the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two. a partition coefficient is the. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT GOLDSCHMIDT’S RULES PowerPoint Presentation ID310825 Partition Coefficient Explained the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to the aqueous layer. what is partition coefficient? a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a substance in one medium or phase (c 1) to the concentration in a second. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Review of Mass Transfer PowerPoint Presentation, free download Partition Coefficient Explained a partition coefficient is the ratio of a solute in two different solvents. Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
6 Values of Partition Coefficient and Classification Entropy Partition Coefficient Explained the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.chegg.com
Solved 1. Explain partitioning coefficient and define the Partition Coefficient Explained the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to the aqueous layer. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. what. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From pubs.acs.org
Calculating Partition Coefficients of Small Molecules in Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient Explained the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to the aqueous layer. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two. in this video animated. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.youtube.com
History and Challenges in determination of partition coefficient YouTube Partition Coefficient Explained in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two. Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate.. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From mungfali.com
Partition Coefficient Phase Diagram Partition Coefficient Explained what is partition coefficient? in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. the partition coefficient is a ratio that describes how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, usually an. the partition. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.youtube.com
Partition coefficient Top 11 Facts YouTube Partition Coefficient Explained a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a substance in one medium or phase (c 1) to the concentration in a second. what is partition coefficient? Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. The ratio. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Estimation of partition coefficient (log P ). (a) Illustration of Partition Coefficient Explained Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. what is partition coefficient? the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. the partition coefficient \(k\) is the ratio of the compound's concentration in the organic layer compared to. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.researchgate.net
Composition, partition coefficient, slope of liquidus and solutal Partition Coefficient Explained Solubility (grams per 100 ml) or molarity concentrations (mole per liter) are often used to evlauate. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. what is partition coefficient? in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. The ratio of a compound’s unionized species. Partition Coefficient Explained.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Partition Coefficients PowerPoint Presentation, free download Partition Coefficient Explained what is partition coefficient? in this video animated explanation of partition coefficient/ distribution law/. The ratio of a compound’s unionized species concentrations in a mixture of two. the partition coefficient, designated p (or, more commonly, log p), is a ratio of the concentration of a compound at. a partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration. Partition Coefficient Explained.